22 February 2023
12155
12 min
5.00

What Is the Digital Customer Experience? A Definition, Trends & Best Practices for 2024
Content
The fast rise of digital channels has created numerous challenges for companies looking to engage with their customers and maintain a positive brand image. This shift towards a more digital landscape has also brought about the need for digital transformation, as companies must adapt and evolve to meet the changing demands and expectations of their customers.
In order to succeed in this new era of customer engagement, businesses must understand what the digital customer journey is, why customer experience is important, and how to leverage technology to create seamless engagement.
What Is the Digital Customer Experience (DCX)
The digital customer experience (DCX) refers to the overall experience a customer has when interacting with a company through its multiple digital channels, such as its website, widgets, mobile apps, social media platforms, and other touchpoints.
The DCX includes not only the functional aspects of the digital experience, such as the ease of use and accessibility but also the emotional and relational aspects, such as the level of personalization and the quality of customer support. The goal of DCX is to create a seamless, consistent, and positive experience for the customer that leaves a lasting impression and drives brand loyalty.
Digital Customer Experience vs. Customer Experience
The digital customer experience and customer experience are similar concepts but have some key differences. CX refers to the overall experience a customer has with a company, including both digital and non-digital interactions.
DCX, on the other hand, is a subset of the overall customer experience, focusing specifically on the customer’s interaction with the company through digital channels. The goal of DCX is to ensure that the digital experience aligns with the overall brand experience and enhances it.
Seven Stages of the Digital Customer Journey
Understanding the different stages of a customer’s interaction with a company’s digital assets is crucial for creating a seamless and effective experience.
1. Awareness
In the awareness stage, customers become aware of a brand or product. This stage is often the starting point of the customer journey and can be influenced by various factors, such as mobile marketing and online advertising.
One of the tools for reaching customers and creating awareness is targeted advertisements, which is when brands deliver advertisements to specific target audiences based on demographics, location, interests, behaviors, and other factors.
2. Interest
In the interest stage, customers start to show an active interest in a company or product and may approach the brand through customer engagement activities, such as visiting a website or following an organization on social media.
For example, brands can use email campaigns to recommend products that the customer is likely to be interested in.

Make personalized emails to engage customers
3. Consideration
In the consideration stage, customers start to evaluate the options available to them and consider the potential benefits and drawbacks of each. Brands can provide information, such as product specifications, to help customers make informed decisions and advance to the next stage of the journey.
4. Intent
In the intent stage, customers express a clear intention to make a purchase. This stage is often accompanied by increased research and evaluation as customers seek to determine the best option for their needs.
Brands can use product demos and trials, which will create the opportunity for customers to try out a product or service and build confidence in their purchase decision.
5. Evaluation
In the evaluation stage, customers make a final assessment of their options and make a decision about which one to choose. Brands can use customer feedback, such as customer satisfaction (CSAT) and online reviews, to improve the customer experience and better meet the needs of their customers.
6. Purchase
In the purchase stage, users complete a transaction and become customers of the brand. Brands can use a number of strategies to encourage customers to complete a purchase and drive sales, including streamlining the checkout process, offering multiple payment options, and providing clear return and refund policies.
7. Loyalty & Advocacy
In the loyalty and advocacy stage, customers continue to engage with the brand and may become brand advocates, spreading the word about their positive experiences.
Brands can use customer analytics, i.e., the net promoter score (NPS), to measure the likelihood of a customer recommending a brand to others. Using the NPS feedback, brands can identify areas for improvement and make changes as required.
How to Improve Digital CX: Tips & Best Practices
Here are some tips and best practices to help you deliver the best digital experience possible.
Fast Loading Times

Customers expect fast loading times. If a website takes too long to load, customers are likely to leave and look for a faster alternative.
To improve the digital CX, brands should focus on optimizing their websites for speed by reducing the number of featured images and videos, compressing content to reduce file sizes, and using a reliable hosting service.
Mobile Optimization
It’s essential for brands to optimize their digital experiences for mobile devices by designing a responsive website that adjusts to different screen sizes, providing easy navigation on small screens, and ensuring that content looks great regardless of how the client accesses it.
As a bonus, mobile optimization can also help improve search engine rankings, as search engines rank websites higher if they are mobile-friendly.
Integrated Omnichannel Experience

An omnichannel experience can help improve the overall customer journey, as customers can easily switch between channels and receive the same level of service and support. For example, if a customer starts shopping on their mobile device, they can easily continue their shopping experience on their desktop computer without losing any of their saved information.
This practice also includes omnichannel marketing to deliver a consistent and cohesive customer experience across all channels, including in-person, online, mobile, and social.
Proactive Customer Service
Proactive customer service involves anticipating customer needs and providing support and assistance before the customer has to ask for it.
It can be sending follow-up emails after a purchase, offering product recommendations based on past purchases, or providing real-time support through chatbots or live chat. By providing proactive customer service, brands can differentiate themselves from competitors and create a more positive customer experience.
Self-Service

Self-service refers to the ability of customers to find answers to their questions or resolve their issues independently without having to engage with customer service. This can be achieved through a variety of self-service tools and resources, such as online knowledge bases, FAQs, chatbots, and community forums.
Continuous Improvement Based on Feedback
Gathering feedback online can be done in many ways: through online surveys, customer reviews, and social media. Once the feedback is collected, it’s essential to analyze it and use it to inform ongoing improvements to the personalized customer experience. This can include changes to the website design, improvements to the customer service process, or the development of new features and functions.
Digital CX Trends to Follow in 2024
To help you stay ahead of the curve, here are the top digital CX trends to follow in 2024. Find out how you can incorporate them into your digital customer experience strategy.
Immersive Experiences
Augmented reality and virtual reality technologies are used to create immersive experiences that engage customers in new and innovative ways. However, businesses must consider factors such as ease of use, device compatibility, and user interface when creating immersive experiences.
Conversational Interfaces
Chatbots, voice assistants, and other conversational interfaces will continue to grow in popularity as the demand for digital customer service increases and customers seek more convenient and accessible ways to engage with brands.
Chatbots, for instance, can handle a large volume of customer queries and provide instant support 24/7, even outside of business hours.
Empathy-Driven Design
This approach to creating a layout of your solution goes beyond just meeting functional requirements. Brands will prioritize empathy-driven design to create a more human-centered digital CX that addresses the emotional and psychological needs of customers. Thus, interactions will resonate with customers on a deeper level, and brands will be able to create more meaningful connections with them.
Privacy and Trust
As consumers become more aware of the potential risks associated with sharing their personal information online, they are demanding greater transparency and security from brands. Therefore, privacy and trust are becoming more important in shaping the future of the online customer experience.
Brands must be transparent about their data collection and usage practices and implement strong privacy measures to protect customer data, including implementing secure data storage systems.
Micro-Moments
Brands will focus on providing relevant and timely experiences during ‘micro-moments.’ These are brief and often spontaneous interactions that take place throughout the customer journey, such as quick searches for information or the need for immediate assistance.
For this, brands must be able to quickly understand the context and intent behind the interaction and provide relevant and timely responses.
Examples of Digital CX
These examples can give you inspiration and guidance as you work to improve your own digital CX strategy.
Omnichannel Experience by Apple

Apple’s omnichannel experience is a prime example of how a company can create a seamless and consistent customer experience across multiple digital channels.
If a customer starts researching a product on the website and wants to continue in person, they can easily find the nearest store, see if the product is in stock, and even make a reservation to try it out. The same happens if a customer needs support.
Omnichannel Experience by ANC Pharmacy
ANC Pharmacy is the leader among pharmacy retailers in Ukraine. They became the first in Ukraine with robotic pharmacies. In addition to the site, the company uses the following channels:
- Mobile app;
- Social media;
- Email, SMS, Rich Messaging;
- Chatbots.
The ANC team decided to make customer communication more effective and increased sales by 87% via rich messaging and by 34% via email with personalized triggers.
Chatbot Conversations by Sephora
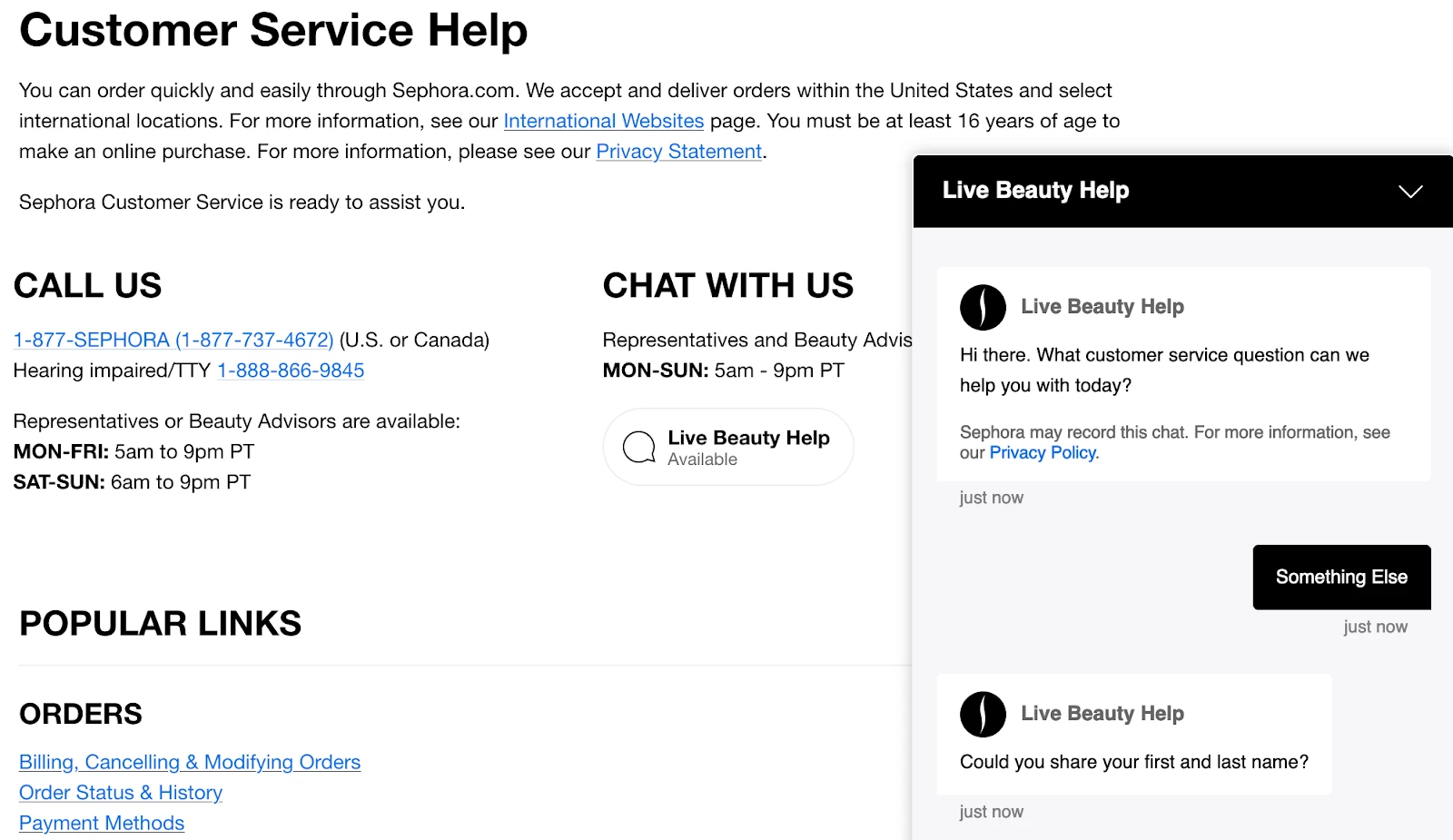
By integrating chatbots into its website and mobile app, Sephora has provided customers with a convenient and easy-to-use platform for answering questions and finding products. Sephora’s chatbots also provide personalized product recommendations based on the customer’s preferences and purchase history.
Virtual Try-On by Nike

The virtual try-on feature uses augmented reality technology and allows customers to see how products would look and fit on their bodies. The feature can be accessed through the Nike app on a smartphone or tablet and eliminates the need for customers to physically visit a store to try on products.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the digital customer experience is a critical aspect of customer engagement in the digital age. By understanding the definition, trends, and best practices, companies can create a seamless and satisfying experience for their customers, driving brand loyalty and long-term success.
Incorporating new technologies, such as artificial intelligence and customer data platforms (CDP), into your DCX strategy can help you stay ahead of the curve and deliver a truly exceptional experience for your customers in 2024 and beyond.
